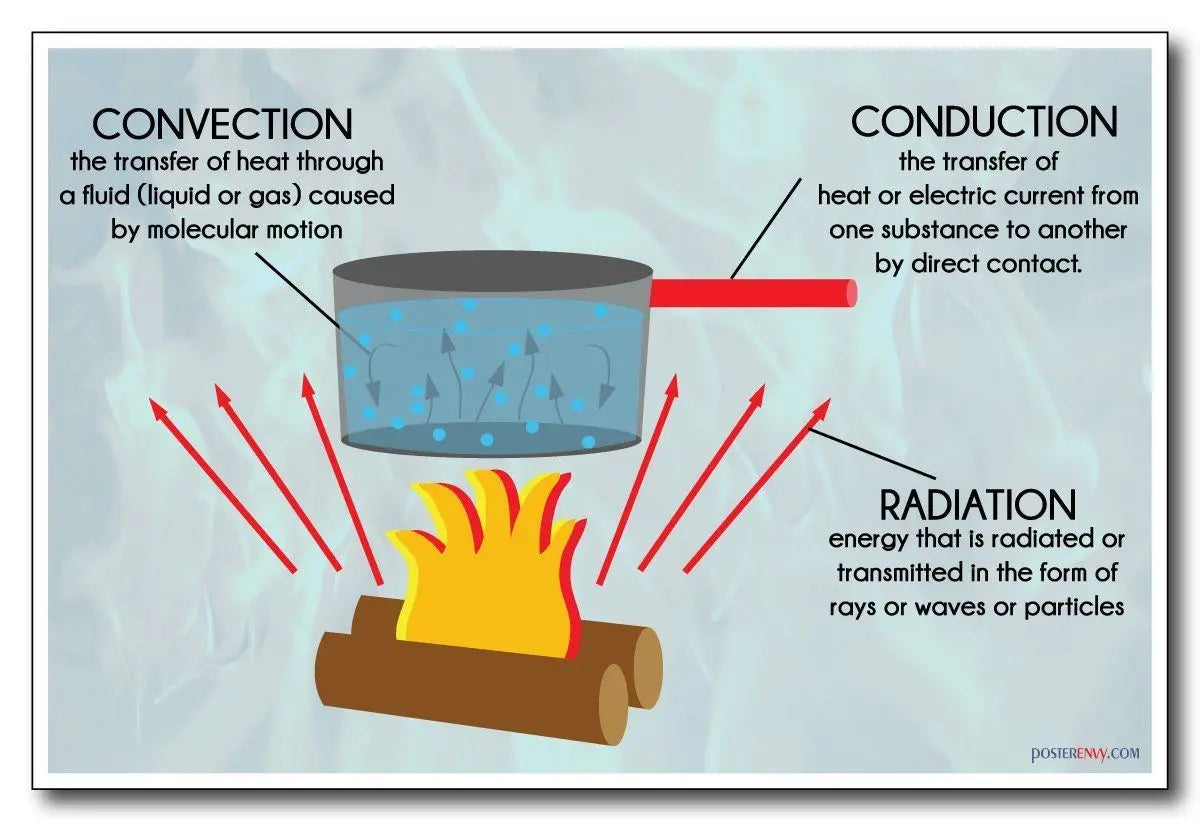
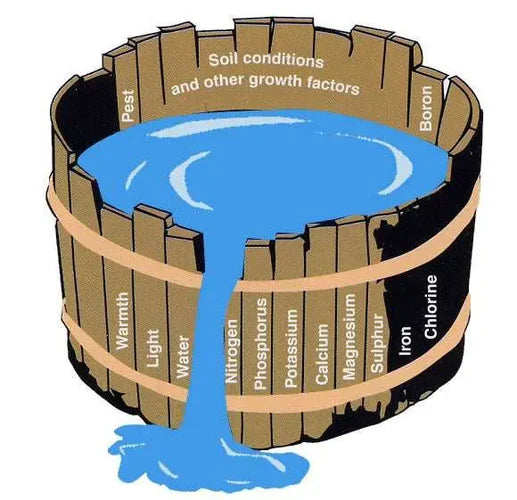
Photosynthesis
Put simply, photosynthesis is a chemical process within a plant which makes food for the plant to live and grow.
To do this the plant requires 3 things - carbon dioxide (CO2), water (H20), and light. The plan...
Read More